Accounting Cycle 8 Steps in the Accounting Cycle, Diagram, Guide

Disorganized books could eventually lead to serious legal or tax liability consequences. Auditing is an independent examination of an organization’s financial records, processes, and internal controls conducted by a qualified external auditor or an internal audit team. The primary role of auditing in the accounting cycle the accounting cycle is to provide an objective assessment of the financial statements’ accuracy and compliance with accounting standards.
The Critical 8 Steps of the Accounting Cycle

However, the following process for tracking activity and creating financial statements doesn’t change. The accounting cycle also plays a vital role in maintaining internal controls, which are procedures designed to safeguard assets, ensure accurate reporting, and prevent fraud. Steps like reconciliation, trial balances, and adjusting entries are integral to these controls. Those financial statements including balance sheet, income statement, statement of change in equity, statements of cash flow, and noted to financial statements.
What is the simple example of the accounting period concept?
![]()
As mentioned, the accounting cycle is made up of 8 well-defined steps that lead to the accurate and timely documentation of a business’s financial performance during a particular accounting period. At the start of the next accounting period, occasionally reversing journal entries are made to cancel out the accrual entries made in the previous period. After the reversing entries are posted, the accounting cycle starts all over again with the occurrence of a new business transaction.
The 8 Steps of the Accounting Cycle
- With the data laid out this way, it’s easy to see if the numbers match up.
- The year-end book includes the year-end financial statements and trial balance, which constitute the results of the year.
- If your team still relies on paper documents or scattered email threads, you’re more likely to miss key details when recording or adjusting transactions.
- If they don’t match, there’s an error somewhere in the recording or posting process.
- Learn the full cycle of the accounts payable process, its key steps, challenges, and how automation can improve efficiency and compliance.
- Whether you use a single entry accounting system or a double entry accounting system, applying a debit or credit to every transaction is necessary.
It is useful to print out the key documents supporting the completed financial statements and store them in a binder. This Debt to Asset Ratio can include all journals, as well as source documents for major journal entries, such as the depreciation calculations. This information provides backup information for the financial statements, and is of particular use when providing evidentiary matter to auditors. This trial balance should contain zero balances for all temporary accounts. The second step in the cycle is to create journal entries for each transaction in chronological order. Point of sale technology can assist in combining steps 1 and 2, but companies might still have to track items like expenses separately.
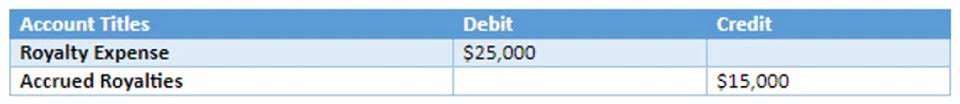
Automatic journal entries can be set up for recurring transactions like monthly insurance expenses, and depreciation entries are generated based on the setup in your accounting system. Complex transactions, such as https://www.bookstime.com/ mergers, require detailed analysis and specific journal entries. An accounting system facilitates various accounting processes such as posting to the general ledger, closing the books, and preparing journal entries. It automates tasks, records transactions, and produces necessary financial reports, ensuring accurate and efficient financial management.


Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!